To become a good doctor, it requires a combination of extensive medical knowledge, practical skills, and a set of personal and professional qualities that go beyond just academic excellence. Here are some key aspects to focus on:
Become A Good Doctor!
- Strong Academic Foundation: Begin with a robust understanding of medical science. This involves completing medical school (MBBS or equivalent), understanding the basics of human anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and other medical sciences.
- Clinical Skills: Develop strong clinical skills through hands-on training. This includes diagnosing illnesses, performing medical procedures, and providing effective treatment plans. Clinical rotations and residencies are crucial for this.
- Lifelong Learning: Medicine is a field that constantly evolves. Stay updated with the latest research, treatments, and medical technologies. Attend workshops, seminars, and continue your education through courses and certifications.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication with patients, families, and healthcare teams is crucial. This includes explaining diagnoses and treatments clearly to patients and collaborating effectively with other healthcare professionals.
- Empathy and Compassion: A good doctor understands and empathizes with patients’ experiences and emotions. Showing compassion can significantly improve patient care and outcomes.
- Ethical Practice: Adhere to high ethical standards. This includes maintaining patient confidentiality, obtaining informed consent, and always acting in the best interest of your patients.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Be adept at critical thinking and quick decision-making, especially in high-pressure situations. This also involves being innovative in diagnostic processes and treatment plans.
- Resilience and Stress Management: The medical profession can be demanding. Develop resilience and strategies to manage stress effectively.
- Leadership and Teamwork: As a doctor, you may need to lead healthcare teams. Cultivate leadership skills and learn how to work efficiently as part of a team.
- Global Health Perspective: Understand healthcare issues from a global perspective, including public health challenges, health policies, and disparities in healthcare access.
- Networking and Mentorship: Build a professional network and seek mentorship. Learning from experienced doctors can provide invaluable insights into medical practice.
Research and Innovation: Engage in medical research to contribute to the advancement of medical science. Innovation in medicine leads to better patient care and healthcare solutions.
Remember, being a good doctor is not just about treating diseases but also about promoting health, preventing illness, and improving the overall quality of life for your patients. Balancing scientific knowledge with compassion and ethical practice is key to a successful and fulfilling career in medicine.
How to Become A Good Doctor!
Becoming a good doctor involves a combination of education, skill development, and personal attributes. Here are key steps and qualities to focus on:
Educational Pathway:
Undergraduate Degree: Begin with a bachelor’s degree, often in a science-related field. This serves as a foundation for medical knowledge.
Medical School: After your undergraduate degree, you must complete medical school. This is where you gain comprehensive medical knowledge and practical experience.
Residency: Following medical school, you’ll enter a residency program in your chosen specialty, which provides intensive training in a specific field of medicine.
Licensing and Certification:
In order to practice, you must pass licensing exams (like the USMLE in the United States) and obtain a medical license.
Continuous education and occasional re-certification might be required depending on the specialty and country of practice.
Developing Essential Skills:
Clinical Skills: Proficiency in diagnosis, treatment plans, and surgical skills (if applicable) is essential.
Communication Skills: Effective communication with patients and other healthcare professionals is crucial.
Problem-Solving Ability: Medical practice often involves quick and critical decision-making.
Attention to Detail: Precision in procedures, diagnosis, and treatment is a must.
Cultivating Personal Qualities:
Empathy and Compassion: Understanding and relating to patients’ experiences and emotions.
Dedication and Resilience: The path is challenging; perseverance is key.
Ethics and Professionalism: Adherence to ethical guidelines and professional standards of practice.
Lifelong Learning: Medicine is ever-evolving, and continuous learning is essential.
Networking and Mentorship:
Building relationships with experienced doctors can provide guidance and open opportunities.
Engaging in professional organizations can offer resources and connections.
Balancing Work and Life:
Learn to manage stress and maintain a healthy work-life balance to avoid burnout.
Research and Innovation:
Participating in medical research can contribute to your field and keep you at the forefront of medical advancements.
Specialization and Continuing Education:
Specializing in a particular area can enhance your expertise.
Continuous education ensures you stay updated with the latest medical practices and technologies.
Remember, being a good doctor is not only about medical knowledge and skills but also about how you interact with patients, handle stress, and adapt to new challenges and advancements in the medical field.
MBBS Admission 2024-25
Fortune Education Offers Opportunity of Medical Education in Abroad
Fortune Education seems to offer opportunities for medical education abroad, which can be an attractive option for many aspiring doctors. Studying medicine abroad can provide various benefits and experiences:
- Exposure to Different Healthcare Systems: Learning in a different country allows you to understand various healthcare models and practices.
- Cultural Competency: Exposure to diverse cultures enhances your ability to work with patients from different backgrounds, improving your communication and empathy skills.
- Global Network: Building connections with medical professionals and students from around the world can offer unique career opportunities and collaborations.
- Advanced Research Opportunities: Some countries might offer advanced research facilities, especially in specialized fields of medicine.
- Quality Education: Many countries have reputable medical schools that offer high-quality education and training.
- Potential Cost Benefits: In some cases, studying abroad can be more cost-effective than medical education in your home country.
- However, there are important considerations to keep in mind:
- Accreditation and Recognition: Ensure the medical school is recognized and accredited by relevant authorities. This is crucial for your degree to be valid in your home country or elsewhere.
- Licensing Exams: Be aware of the licensing requirements in your home country. You may need to pass additional exams to practice medicine after studying abroad.
- Language Barrier: Consider the language of instruction and the language spoken in the country. Proficiency in the local language might be necessary for clinical rotations.
- Cultural Adaptation: Living and studying in a new country requires adjustments and can be challenging alongside the rigorous demands of medical education.
- Financial Considerations: Factor in the cost of living abroad, travel, and potential differences in tuition fees.
If you are considering an opportunity through Fortune Education or any other agency, it’s crucial to do thorough research and due diligence. Check the credentials of the agency, the accreditation of the medical schools they partner with, and seek reviews or testimonials from students who have gone through their programs. Additionally, understanding the post-graduation pathways for practicing medicine in your desired location or back home is essential.
Get Online Direct MBBS Admission in Bangladesh and Abroad
If you’re interested in pursuing MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery) admission in Bangladesh or abroad through an online direct admission process, here are some steps and important considerations:
Research Accredited Institutions:
Identify accredited medical schools in Bangladesh and other countries. Accreditation ensures the institution meets specific educational standards, which is crucial for your degree’s validity and recognition.
Understand Eligibility Criteria:
Each institution and country may have different eligibility criteria. Common requirements include a high school diploma with science subjects (Physics, Chemistry, Biology), and sometimes, a pre-medical course.
Some countries or universities might require passing an entrance exam like NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) or an equivalent.
Online Application Process:
Visit the official websites of the medical schools to understand their application process.
Prepare necessary documents such as academic transcripts, letters of recommendation, a statement of purpose, and proof of language proficiency if required.
Language Proficiency:
If the course is offered in a language other than your native one, you may need to prove proficiency through tests like IELTS or TOEFL.
Understand the Fee Structure:
Investigate the tuition fees, accommodation costs, and other living expenses. This will help in planning your finances and any scholarships or financial aid available.
Licensing and Recognition:
Ensure that the degree offered is recognized by the medical council or equivalent authority in your home country or where you plan to practice medicine.
Be aware of the licensing process in the country where you intend to practice after graduation.
Visa and Accommodation:
For studying abroad, understand the visa requirements and process.
Research accommodation options, either on-campus or nearby.
Beware of Fraudulent Practices:
Be cautious of agencies or individuals promising guaranteed admissions or shortcuts. Always verify information and go through official channels.
Seek Guidance:
Contact the admissions office of the universities for any queries.
Consider speaking with current students or alumni of the program for insights.
Cultural and Educational Preparedness:
Prepare yourself for cultural differences and educational styles in a new country. It’s part of the learning experience and personal growth.
Regular Updates:
Keep track of application deadlines, interview dates, and any required entrance exams.
Remember, pursuing medical education, especially abroad, is a significant commitment and investment. It’s crucial to thoroughly research and understand all aspects of the program and life in the host country to make an informed decision.
MBBS Admission Criteria in Bangladesh, Nepal, Kazakhstan and India
MBBS admission criteria can vary significantly between countries like Bangladesh, Nepal, Kazakhstan, and India. Here’s a general overview of the typical admission requirements in each of these countries:
MBBS Admission in Bangladesh
- Academic Requirements:
- High school diploma with a strong background in science, particularly in Biology, Chemistry, and Physics.
A minimum GPA, often around 3.5 out of 5.0, but this can vary by institution.
Entrance Exams: - Some universities might require an admission test.
Age Limit: - Generally, there is a minimum age requirement, often 17 years.
Medical Fitness: - Applicants may need to pass a medical fitness test.
MBBS Admission in Nepal
- Academic Requirements:
- Completion of higher secondary education (10+2) with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
Minimum marks requirements vary, typically around 50% in aggregate.
Entrance Exams: - NEET (for Indian students) or similar entrance tests for local and international students.
Some universities conduct their own admission tests.
Age Limit: - Usually, the minimum age is 17 years.
Medical Fitness: - Medical fitness certification might be required.
MBBS Admission in Kazakhstan
Academic Requirements:
Completion of high school with a good record in science subjects.
Some universities may specify minimum grade requirements.
Entrance Exams:
Not all universities require an entrance exam. However, some might have their own testing or interviews.
Language Proficiency:
Since some programs are in English, non-native speakers might need to prove English proficiency.
Medical Fitness:
A general health check-up may be required.
MBBS Admission in India
Academic Requirements:
Completion of 10+2 with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology/Biotechnology.
Minimum marks usually 50% in aggregate in these subjects.
Entrance Exams:
NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) is mandatory for all aspirants, including for private colleges and deemed universities.
Age Limit:
The minimum age is generally 17 years.
Domicile and Reservation Policies:
State-level quotas and reservation policies may apply in government colleges.
Medical Fitness:
Medical fitness certification is required.
General Tips:
Research Specific Universities: Admission criteria can vary between universities within the same country, so it’s important to check the specific requirements of each institution you’re interested in.
Prepare for Entrance Exams: If the country or university of your choice requires an entrance exam, dedicate ample time for preparation.
Language Proficiency: If you’re applying to a program in a non-native language, ensure you meet any language requirements.
Stay Updated: Admission criteria and processes can change, so it’s important to refer to the latest information from official university or government education websites.
Each country offers unique advantages and challenges for MBBS students, so consider your options carefully based on your academic background, career goals, and personal preferences.
MBBS Fees Structure in Abroad
The fees structure for MBBS programs abroad can vary widely depending on the country, university, and specific program. Here’s a general overview of what you might expect in different regions:
1. Eastern Europe (e.g., Russia, Ukraine, Georgia)
Tuition Fees: Approximately $3,000 to $8,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Around $200 to $300 USD per month.
2. Central Asia (e.g., Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan)
Tuition Fees: Approximately $2,000 to $6,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Around $100 to $300 USD per month.
3. South Asia (e.g., Bangladesh, Nepal)
Tuition Fees:
In Bangladesh, it can range from $3,000 to $10,000 USD per year.
In Nepal, the cost ranges from $25,000 to $70,000 USD for the total course.
Living Costs: Generally, around $100 to $250 USD per month.
4. Southeast Asia (e.g., Philippines, Malaysia)
Tuition Fees: Approximately $1,200 to $5,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Around $200 to $400 USD per month.
5. China
Tuition Fees: Around $2,000 to $10,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Approximately $200 to $400 USD per month.
6. Caribbean
Tuition Fees: Varies widely, from about $15,000 to over $25,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Can range from $500 to $1,000 USD per month.
7. Western Europe (e.g., Germany, Italy)
Tuition Fees:
In countries like Germany, education is often subsidized, but language proficiency in German is a must.
In Italy and other Western European countries, fees can range from $1,000 to $20,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Approximately $800 to $1,200 USD per month.
8. United Kingdom
Tuition Fees: Around $30,000 to $50,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Approximately $1,200 to $1,500 USD per month.
9. United States and Canada
Tuition Fees: Among the highest, generally ranging from $25,000 to $70,000 USD per year.
Living Costs: Around $1,000 to $2,000 USD per month.
Key Points to Remember:
Currency Fluctuations: The costs can vary due to changes in currency exchange rates.
Additional Costs: Consider additional expenses like health insurance, travel, books, and other educational materials.
Scholarships and Financial Aid: Some universities offer scholarships, which can significantly reduce the financial burden.
Quality of Education vs. Cost: Higher cost doesn’t always equate to better quality. Research the university’s reputation, quality of education, and the recognition of the degree.
When considering studying MBBS abroad, it’s essential to look at the total cost of education, including living expenses, and not just the tuition fees. Additionally, understand the long-term implications, such as the recognition of the degree in your home country or elsewhere, post-graduation career opportunities, and the quality of clinical training.
Medical Education in Bangladesh
Medical education in Bangladesh, particularly the training required to become a doctor, follows a structured pathway and adheres to certain standards and practices. Here’s an overview of how medical education typically works in Bangladesh:
Pre-Medical Education:
Before entering medical school, students usually complete their Higher Secondary Certificate (HSC) with a focus on science subjects, especially biology, chemistry, and physics.
Achieving good grades in these subjects, along with a strong overall academic record, is crucial for eligibility in medical colleges.
Medical College Admission Test:
Aspiring medical students must sit for a competitive admission test, which is essential for securing a place in a medical college.
The test assesses knowledge in subjects like biology, chemistry, physics, and general aptitude.
MBBS Program:
The standard program to become a doctor in Bangladesh is the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS).
The MBBS program typically lasts for five years.
The curriculum includes basic medical sciences (like anatomy, physiology, biochemistry) in the initial years, followed by clinical subjects (such as medicine, surgery, pediatrics, and obstetrics) in the later years.
Internship Training:
After completing the MBBS course, there is usually a mandatory one-year internship.
This internship provides hands-on clinical experience in various departments and is essential for practical training.
Licensing:
Graduates must register with the Bangladesh Medical and Dental Council (BM&DC) to practice legally as doctors.
The registration process involves verification of qualifications and sometimes an examination.
Specialization and Postgraduate Training:
Doctors looking to specialize in a particular field can pursue postgraduate training, such as a Master of Surgery (MS) or Doctor of Medicine (MD), or other diploma courses.
Admission to these programs is competitive and often requires additional entrance examinations.
Continuing Medical Education (CME):
Practicing doctors are expected to continue their education to stay updated with the latest developments in medical science.
CME can include attending workshops, seminars, and conferences.
Research Opportunities:
There are opportunities for medical research, and students and professionals are encouraged to engage in research activities to contribute to the medical field.
Quality and Standards:
The quality of medical education in Bangladesh varies among institutions. Some are renowned for their high standards and competitive admission processes.
There’s a growing emphasis on improving the quality of medical education and healthcare services in the country.
Challenges:
Challenges in medical education in Bangladesh include a high student-to-teacher ratio, the need for more modern equipment and facilities in some institutions, and the necessity for more research-focused education.
Overall, medical education in Bangladesh is designed to create competent and skilled healthcare professionals capable of addressing the health needs of the population. As with any country, there are areas of strength as well as challenges that are being addressed over time.
MBBS Admission Bangladesh
Gaining admission to the MBBS program in Bangladesh involves a series of steps and meeting certain criteria. The process is competitive and requires careful planning and preparation. Here’s a general guide to the MBBS admission process in Bangladesh:
Eligibility Criteria:
Academic Requirements: Candidates typically must have completed 12 years of schooling with a focus on science subjects, particularly Biology, Chemistry, and Physics.
Minimum Grades: There’s usually a minimum grade or GPA requirement in both the SSC (Secondary School Certificate) and the HSC (Higher Secondary Certificate) exams, often with a higher emphasis on science subjects.
Age Limit: Some institutions may have an age limit for applicants.
Entrance Exam:
Candidates must pass a medical college admission test, which is highly competitive.
The exam usually tests knowledge in subjects like Biology, Chemistry, Physics, and English, and may also include general knowledge or aptitude questions.
Application Process:
The application for medical colleges in Bangladesh is typically done through a centralized system managed by the Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS).
Applicants need to fill out an online application form and submit it within the specified deadline.
Documentation:
Essential documents usually include academic transcripts, test scores, proof of nationality (like a passport for international students), and recent photographs.
Some colleges might require additional documents, so it’s important to check the specific requirements of each college.
Selection Process:
Selection for MBBS admission is primarily based on the scores obtained in the entrance exam.
Academic performance in SSC and HSC examinations may also be considered.
Medical Fitness:
Candidates must be medically fit. A medical examination is often part of the admission process.
Admission for International Students:
International students usually have a separate quota and may have different admission requirements.
They might need to provide additional documentation, such as equivalence certificates for their educational qualifications.
Fees and Financial Planning:
The cost of studying MBBS in Bangladesh varies between colleges. It’s important to get detailed fee information from the specific college.
International students generally pay higher fees than local students.
Visa Process for International Students:
International students need to obtain a student visa. The admission letter from the college is typically required for the visa application.
Language of Instruction:
The medium of instruction in most medical colleges in Bangladesh is English, especially for international students. However, some familiarity with Bengali might be beneficial.
It’s important to regularly check the DGHS website or the websites of individual medical colleges for the most current information on admission processes, dates, and requirements. The criteria and processes may vary slightly from year to year.
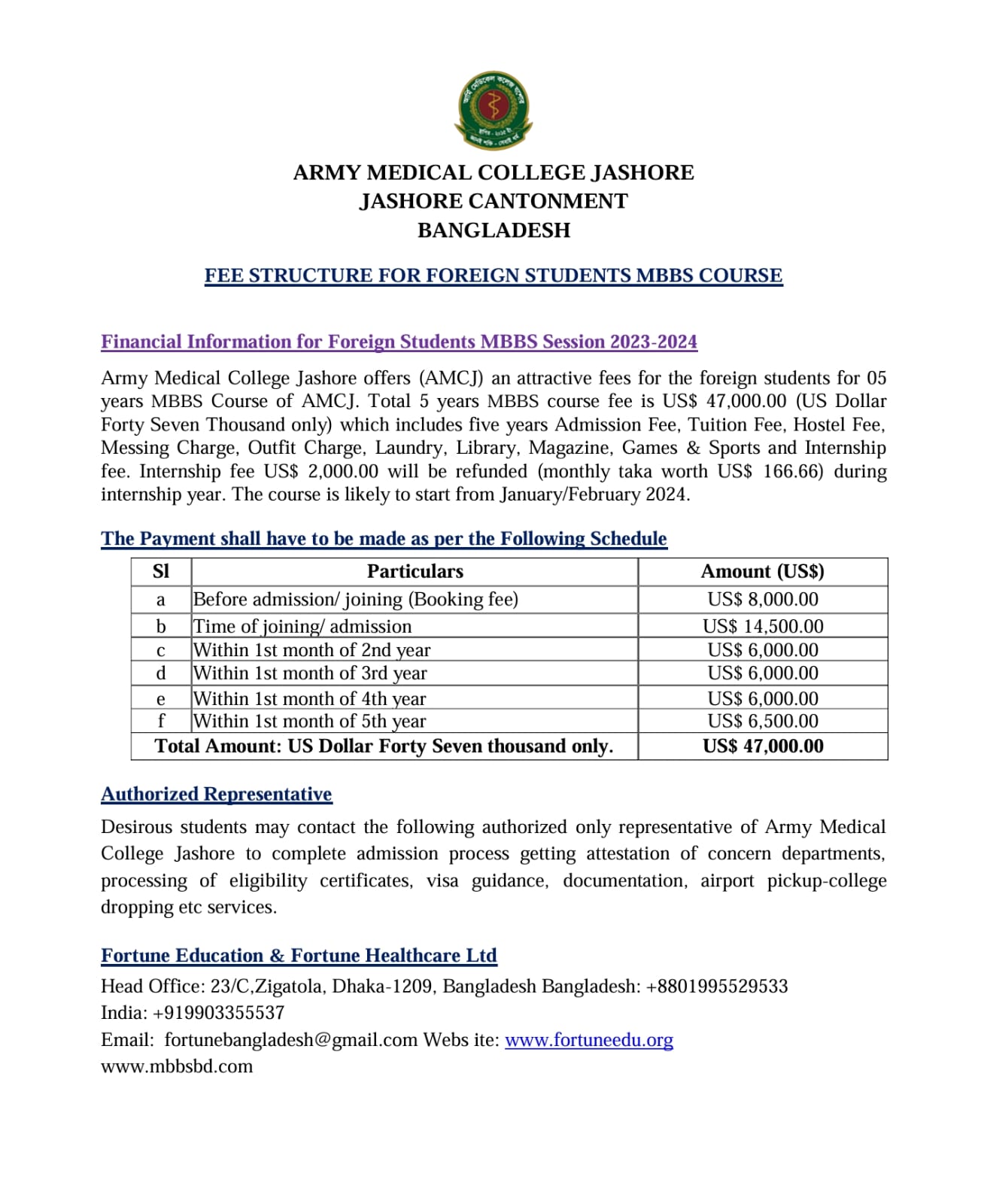
Best Army Medical Colleges 1. Army Medical College Bogura 2. Army Medical College Cumilla Army Medical College 3. Army Medical College Jashore
When discussing the best Army Medical Colleges in Bangladesh, it’s important to consider various factors such as academic quality, facilities, faculty expertise, and overall reputation. The three institutions you mentioned – Army Medical College Bogura, Army Medical College Cumilla, and Army Medical College Jashore – are part of the Bangladesh Army’s initiative to provide top-notch medical education and training. Here’s a brief overview of each:
Army Medical College Bogura (AMCB)
- Location: Situated in Bogura, a significant city in the Rajshahi Division in Bangladesh.
Establishment: Like other Army Medical Colleges, AMCB was established to address the growing need for skilled medical professionals in the country. - Facilities: The college likely offers modern classrooms, well-equipped laboratories, extensive libraries, and possibly ties with nearby military hospitals for clinical training.
Reputation: As an Army Medical College, AMCB would be expected to maintain a high standard of discipline and academic excellence.
Army Medical College Cumilla (AMCCu)
Location: Located in Cumilla, known for its historical and cultural significance in Bangladesh.
Features: AMCCu would typically have state-of-the-art educational facilities, including advanced medical training equipment and resources for research and development.
Clinical Training: Strong emphasis on hands-on clinical experience, likely facilitated through affiliated hospitals.
Academic Environment: The institution likely fosters a disciplined, rigorous academic environment, characteristic of military-run educational establishments.
Army Medical College Jashore (AMCJ)
- Location: Based in Jashore, an important city in the Khulna Division.
Curriculum and Training: AMCJ probably offers a comprehensive curriculum that includes both theoretical and practical medical training.
Faculty: The faculty likely includes experienced and well-qualified professionals in various medical disciplines. - Overall Development: Emphasis on the holistic development of students, including extracurricular activities and leadership skills, in addition to academic excellence.
- When comparing these colleges, consider the following factors:
- Academic Programs: Look into the specific programs and specializations offered by each college.
Clinical Exposure: Evaluate the opportunities for practical training and real-world medical experience. - Faculty Expertise: Consider the qualifications and experience of the teaching staff.
- Facilities and Resources: Assess the quality of laboratories, libraries, and other educational resources.
- Student Feedback: If possible, seek feedback from current students or alumni about their experiences.
- Location and Accessibility: The geographic location might be a factor depending on your personal or logistical preferences.